Install fastq-dl
To easily download fastq from GEO or ENA, use fastq-dl
Assume you already have conda installed, do the following:
conda config --add channels conda-forge
conda config --add channels bioconda
conda create -n fastq_download -c conda-forge -c bioconda fastq-dl
conda activate fastq_download Tip: use mamba if conda is too slow for you.
They are all big snakes!!
We will use bulk RNAseq data from this GEO accession ID: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE197576
mkdir hypoxia_RNAseq
cd hypoxia_RNAseq
mkdir data
cd data
## some times the same experiment may have multiple runs (SRR)
## use the --group-by-experiment to merge them, this example only has one SRR
## per sample
## normoxia sgCTRL
fastq-dl --accession SRX14311105 --group-by-experiment
fastq-dl --accession SRX14311106 --group-by-experiment
## hypoxia sgCTRL
fastq-dl --accession SRX14311111 --group-by-experiment
fastq-dl --accession SRX14311112 --group-by-experimentWe only have 4 samples here and we typed in the command one by one which is fine. What if we want to process all of them and you do not want to do it manually.
Get the metadata using SRA Run selector or use GEOquery or GEOmetadb.
You may want to do a fastqc for quality control of the reads and trimming with
fastp for the sequencing adapters. We will skip it in this tutorial.
install salmon
conda create -n salmon salmonbuild an index
We need a transcriptome fasta file to build the index, we also need the gtf file that we can use to map gene ids.
Let’s go to gencode https://www.gencodegenes.org/human/
There are multiple sources to get the reference files. If you are confused, watch this video.
Download the reference fasta:
cd hypoxia_RNAseq
mkdir reference
cd reference
wget https://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/databases/gencode/Gencode_human/release_45/gencode.v45.annotation.gtf.gz
wget https://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/databases/gencode/Gencode_human/release_45/gencode.v45.basic.annotation.gtf.gzA quick look at the gtf file:
zless -S gencode.v45.annotation.gtf.gz | grep -v "#" | \
awk '$3=="gene"' | cut -f9 | head -3
gene_id "ENSG00000290825.1"; gene_type "lncRNA"; gene_name "DDX11L2"; level 2; tag "overlaps_pseudogene";
gene_id "ENSG00000223972.6"; gene_type "transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene"; gene_name "DDX11L1"; level 2; hgnc_id "HGNC:37102"; havana_gene "OTTHUMG00000000961.2";
gene_id "ENSG00000227232.6"; gene_type "unprocessed_pseudogene"; gene_name "WASH7P"; level 2; hgnc_id "HGNC:38034"; havana_gene "OTTHUMG00000000958.1";Let’s tally the gene_type
zless -S gencode.v45.annotation.gtf.gz | grep -v "#" | \
awk '$3=="gene"' | cut -f9 | \
cut -f2 -d ";" | sort | uniq -c | sort -k1,1nr
20049 gene_type "protein_coding"
19370 gene_type "lncRNA"
10143 gene_type "processed_pseudogene"
2604 gene_type "unprocessed_pseudogene"
2208 gene_type "misc_RNA"
1901 gene_type "snRNA"
1879 gene_type "miRNA"
1054 gene_type "TEC"
962 gene_type "transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene"
942 gene_type "snoRNA"
513 gene_type "transcribed_processed_pseudogene"
497 gene_type "rRNA_pseudogene"
187 gene_type "IG_V_pseudogene"
158 gene_type "transcribed_unitary_pseudogene"
145 gene_type "IG_V_gene"
107 gene_type "TR_V_gene"
100 gene_type "unitary_pseudogene"
79 gene_type "TR_J_gene"
49 gene_type "scaRNA"
47 gene_type "rRNA"
37 gene_type "IG_D_gene"
33 gene_type "TR_V_pseudogene"
22 gene_type "Mt_tRNA"
19 gene_type "artifact"
18 gene_type "IG_J_gene"
14 gene_type "IG_C_gene"
9 gene_type "IG_C_pseudogene"
8 gene_type "ribozyme"
6 gene_type "TR_C_gene"
5 gene_type "TR_D_gene"
5 gene_type "sRNA"
4 gene_type "TR_J_pseudogene"
4 gene_type "vault_RNA"
3 gene_type "IG_J_pseudogene"
2 gene_type "Mt_rRNA"
2 gene_type "translated_processed_pseudogene"
1 gene_type "IG_pseudogene"
1 gene_type "scRNA"We will use the gtf file for downstream analysis.
Download the transcript fasta file
wget https://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/databases/gencode/Gencode_human/release_45/gencode.v45.transcripts.fa.gz
index the transcriptome
# list all the conda env
conda env list
# activate the salmon env
conda activate salmon
salmon index -t gencode.v45.transcripts.fa.gz -i gencode.v45_human_index -k 31 --gencodequantification
This is a single end read dataset, so I used -r to feed in the fastq. If you
have paired-end reads, you need to use -1 and -2 for the R1 and R2 reads.
There are also different library types for paired end reads. read the documentation for details.
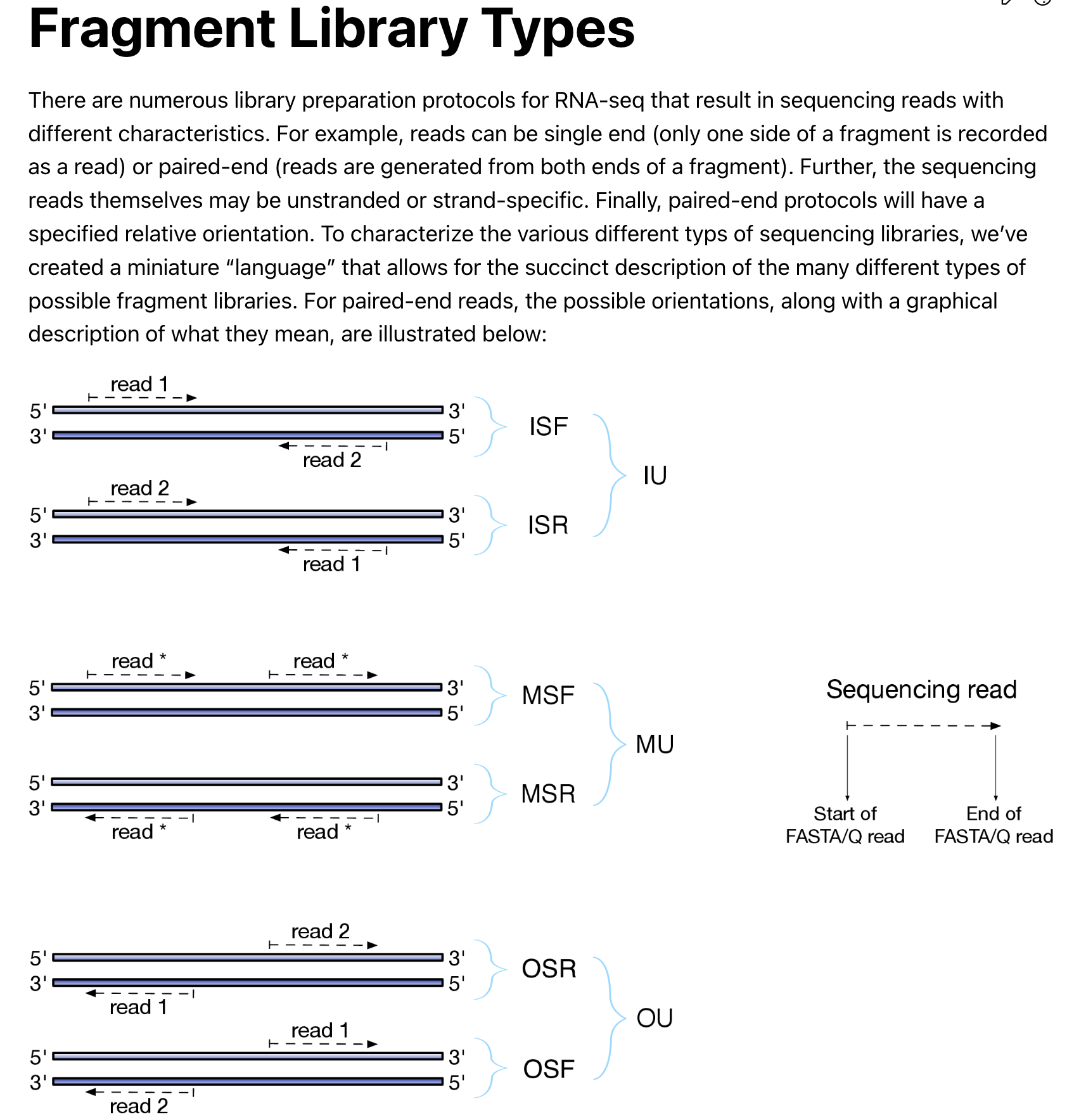
Make sure you know how the library is constructed. I do not know if this library
is stranded or unstranded, so I used -l A to automatically let
salmon to detect the library type. salmon detected it as U unstranded.
cd ..
salmon quant -i reference/gencode.v45_human_index/ -l A -r SRX14311105.fastq.gz -o SRX14311105_quant --validateMappingsThis finished in a couple of mins, so fast!
cat SRX14311105_quant/logs/salmon_quant.log | grep "Mapping rate"
[jointLog] [info] Mapping rate = 93.0329%93% mapping rate!
Let’s do the same for the other 3 samples
salmon quant -i reference/gencode.v45_human_index/ -l A -r SRX14311106.fastq.gz -o SRX14311106_quant --validateMappings
salmon quant -i reference/gencode.v45_human_index/ -l A -r SRX14311111.fastq.gz -o SRX14311111_quant --validateMappings
salmon quant -i reference/gencode.v45_human_index/ -l A -r SRX14311112.fastq.gz -o SRX14311112_quant --validateMappingsNow we have the salmon quantification output:
find . -name "*sf"
./SRX14311111_quant/quant.sf
./SRX14311105_quant/quant.sf
./SRX14311106_quant/quant.sf
./SRX14311112_quant/quant.sfand the mapping rates are all pretty high:
find . -name "salmon_quant.log" | xargs grep "Mapping rate"
./SRX14311111_quant/logs/salmon_quant.log:[jointLog] [info] Mapping rate = 91.5163%
./SRX14311105_quant/logs/salmon_quant.log:[jointLog] [info] Mapping rate = 93.0329%
./SRX14311106_quant/logs/salmon_quant.log:[jointLog] [info] Mapping rate = 92.8808%
./SRX14311112_quant/logs/salmon_quant.log:[jointLog] [info] Mapping rate = 91.4357%we can load it into R and use DESeq2for downstream analysis. That’s for another post!
Happy Learning!
Watch the video here: